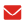
Power station loss based on photovoltaic array absorption loss and inverter loss
In addition to the impact of resource factors, the output of photovoltaic power plants is also affected by the loss of power station production and operation equipment. The greater the power station equipment loss, the smaller the power generation. The equipment loss of photovoltaic power station mainly includes four categories: photovoltaic square array absorption loss, inverter loss, power collection line and box transformer loss, booster station loss, etc.
(1) The absorption loss of the photovoltaic array is the power loss from the photovoltaic array through the combiner box to the DC input end of the inverter, including photovoltaic component equipment failure loss, shielding loss, angle loss, DC cable loss, and combiner box branch loss;
(2) Inverter loss refers to the power loss caused by inverter DC to AC conversion, including inverter conversion efficiency loss and MPPT maximum power tracking capability loss;
(3) The power collection line and box transformer loss are the power loss from the AC input end of the inverter through the box transformer to the power meter of each branch, including the inverter outlet loss, box transformer conversion loss and in-plant line loss;
(4) The booster station loss is the loss from the power meter of each branch through the booster station to the gateway meter, including main transformer loss, station transformer loss, bus loss and other in-station line losses.
After analyzing the October data of three photovoltaic power plants with a comprehensive efficiency of 65% to 75% and an installed capacity of 20MW, 30MW and 50MW, the results show that the photovoltaic array absorption loss and inverter loss are the main factors affecting the output of the power station. Among them, the photovoltaic array has the largest absorption loss, accounting for about 20~30%, followed by inverter loss, accounting for about 2~4%, while the power collection line and box transformer loss and booster station loss are relatively small, with a total of about Accounted for about 2%.
Further analysis of the above-mentioned 30MW photovoltaic power station, its construction investment is about 400 million yuan. The power loss of the power station in October was 2,746,600 kWh, accounting for 34.8% of the theoretical power generation. If calculated at 1.0 yuan per kilowatt-hour, the total in October The loss was 4,119,900 yuan, which had a huge impact on the economic benefits of the power station.
How to reduce the loss of photovoltaic power station and increase power generation
Among the four types of losses of photovoltaic power plant equipment, the losses of the collection line and box transformer and the loss of the booster station are usually closely related to the performance of the equipment itself, and the losses are relatively stable. However, if the equipment fails, it will cause a large loss of power, so it is necessary to ensure its normal and stable operation. For photovoltaic arrays and inverters, the loss can be minimized through early construction and later operation and maintenance. The specific analysis is as follows.
(1) Failure and loss of photovoltaic modules and combiner box equipment
There are many photovoltaic power plant equipment. The 30MW photovoltaic power plant in the above example has 420 combiner boxes, each of which has 16 branches (total of 6720 branches), and each branch has 20 panels (total of 134,400 batteries) Board), the total amount of equipment is huge. The greater the number, the higher the frequency of equipment failures and the greater the power loss. Common problems mainly include burnt out of photovoltaic modules, fire on the junction box, broken battery panels, false welding of leads, faults in the branch circuit of the combiner box, etc. In order to reduce the loss of this part, on the one hand, we must strengthen the completion acceptance and ensure through effective inspection and acceptance methods. The quality of power station equipment is related to the quality, including the quality of the factory equipment, equipment installation and arrangement that meet the design standards, and the construction quality of the power station. On the other hand, it is necessary to improve the intelligent operation level of the power station and analyze the operating data through intelligent auxiliary means to find out in time Fault source, carry out point-to-point troubleshooting, improve the work efficiency of operation and maintenance personnel, and reduce power station losses.
(2) Shading loss
Due to factors such as the installation angle and arrangement of the photovoltaic modules, some photovoltaic modules are blocked, which affects the power output of the photovoltaic array and leads to power loss. Therefore, during the design and construction of the power station, it is necessary to prevent the photovoltaic modules from being in the shadow. At the same time, in order to reduce the damage to the photovoltaic modules by the hot spot phenomenon, an appropriate amount of bypass diodes should be installed to divide the battery string into several parts, so that the battery string voltage and The current is lost proportionally to reduce the loss of electricity.
(3) Angle loss
The inclination angle of the photovoltaic array varies from 10° to 90° depending on the purpose, and the latitude is usually selected. The angle selection affects the intensity of solar radiation on the one hand, and on the other hand, the power generation of photovoltaic modules is affected by factors such as dust and snow. Power loss caused by snow cover. At the same time, the angle of photovoltaic modules can be controlled by intelligent auxiliary means to adapt to changes in seasons and weather, and maximize the power generation capacity of the power station.
(4) Inverter loss
Inverter loss is mainly reflected in two aspects, one is the loss caused by the conversion efficiency of the inverter, and the other is the loss caused by the MPPT maximum power tracking capability of the inverter. Both aspects are determined by the performance of the inverter itself. The benefit of reducing the loss of the inverter through later operation and maintenance is small. Therefore, the equipment selection at the initial stage of the construction of the power station is locked, and the loss is reduced by selecting the inverter with better performance. In the later operation and maintenance stage, the operation data of the inverter can be collected and analyzed through intelligent means to provide decision support for the equipment selection of the new power station.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that losses will cause huge losses in photovoltaic power plants, and the overall efficiency of the power plant should be improved by reducing losses in key areas first. On the one hand, effective acceptance tools are used to ensure the quality of the equipment and construction of the power station; on the other hand, in the process of power station operation and maintenance, it is necessary to use intelligent auxiliary means to improve the production and operation level of the power station and increase the power generation.
Post time: Dec-20-2021